Profitability, Solvency, Liquidity: Understanding Financial Health
To understand the financial health of a company, you need insight into the complete financial structure of a company, the relationship between the various financial values within the company.
Every company needs this information to make (profit) forecasts, budgets and plans for the future, but also to estimate financial risks, such as market risks, credit risks and operational risks. To determine a (financial) strategy based on these insights.
The best way to do this is to calculate so-called financial ratios.

What are financial ratios
By ratio we mean the relationship between (two) numbers, in this case financial values. Calculating a ratio makes it easier to compare results.
Profitability, liquidity, solvency are so-called financial ratios and they are important for assessing the company's results, financial health.
They provide a complete picture of the performance, stability and sustainability of a company.
What are financial ratios useful for
A company’s management will regularly analyze these ratios to monitor profitability, identify potential problems, and take proactive measures. They use these ratios to make informed decisions and assess risks, for example in an investment issue.
Financial ratios, such as profitability, solvency, and liquidity, are important for internal stakeholders, such as management, but also for external stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and suppliers.

What financial ratios are there
There are many ratios that you can use to indicate just as many different financial relationships and relations within your financial structure. Such as:
- efficiency ratios (for example, the turnover ratio and inventory turnover rate),
- growth and sustainability ratios (for example, the dividend yield), market value ratios (for example, the price-earnings ratio and the price-to-book ratio),
- cash flow ratios (for example, the operating cash flow ratio and the cash flow coverage of debt).
But the most important and most used are the ratios for liquidity, solvency and profitability, which I will discuss in more detail now.
What does profitability mean
Profitability calculates the degree of profitability or return of a company and is often expressed as a percentage. Profitability indicates how much profit a company makes compared to its costs and investments.
It is also often used to assess the financial health and performance of a company (interim). Ratios are used to compare current performance with industry averages or those from previous periods. Of course, you need a positive, healthy profitability to be able to exist and grow.

Most common profitability ratios
- Gross Profitability: is the return on (gross) profit, the ratio of sales to the costs of that sales.
- Operating Profitability: This shows the profitability after deducting the operational, fixed costs for the company, such as personnel costs, rent, office supplies, etc.
- Net Profitability: This is a broader measure that relates net profit to total sales. It takes into account all costs, including taxes and interest charges.
- Return on Assets (ROA): ROA indicates how efficiently a company uses its assets, that is, all the assets of a company, both money and resources, to generate profit.
- Return on Equity (ROE): ROE indicates how much return shareholders earn on an investment.

What does solvency mean
Solvency indicates whether a company is able to meet its long-term financial obligations, i.e. can repay long-term debts and not go bankrupt. Solvency indicates what part of a company's total invested capital is equity.
Good solvency means that a company has a lot of invested equity instead of borrowed, debt capital. The company can meet a large part of its obligations with equity, which gives creditors and investors confidence, among other things.
How to calculate solvency
The solvency ratio is calculated by dividing total equity by total assets and multiplying the result by 100 to obtain a percentage.
Solvency = (equity : total assets) x 100
A solvency ratio of 100% means that all of a company's resources are financed by equity, while a ratio of less than 100% indicates what portion of the company's resources are financed by borrowed capital (borrowed money, debts).
What does liquidity mean
The liquidity of a company indicates whether it is able to make payments. So whether it has financial resources or (current) assets available, such as a positive bank/savings balance, receivables and inventories, which can be converted into cash without (much) loss of value.
Higher liquidity generally means that a company has sufficient financial resources to meet obligations, which of course gives confidence. Low liquidity indicates that difficulties may arise in meeting obligations.

What is current ratio
The current ratio shows the relationship between a company's short-term assets and short-term debts or liabilities.
It is calculated using the following formula:
Current ratio = short-term assets : short-term liabilities
A current ratio higher than 1 indicates that a company has more short-term (current) assets than short-term debts and other liabilities, and can therefore make all payments in the coming short period. A ratio of 2 is often considered really healthy or safe.
What is quick ratio
The quick ratio, also known as the acid test ratio, indicates whether a company has (sufficient) financial resources (current assets) to be able to meet payment obligations immediately (quickly). So without the proceeds from the sale of inventory, because selling it normally takes longer.
The quick ratio is calculated using the following formula:
Quick ratio = (cash + accounts receivable + short-term investments): current liabilities
With a quick ratio of 1.0, a company is able to meet all its immediately payable obligations regarding short-term debts, and that gives confidence. In general, a quick ratio of 1.0 or higher is used as a basis for stable business operations.

What is the relationship between liquidity - solvency - profitability
For healthy and financially stable business operations, a company must pay attention to all three ratios, i.e. the relationships (among them). For example: high profitability, the 'interest payment' on the investment of time and money, is of course nice, but it should not be at the expense of solvency or liquidity.
In other words, when spending (parts of) the profit, you must always take into account that there is enough money 'in cash' to meet long-term obligations (solvency) and short-term obligations (liquidity), so as not to get into financial trouble.
Financial Ratios and Corporate Governance
Financial ratios are used by management teams for decision-making and strategic planning, to identify opportunities and risks, and to ensure sound financial management for the growth and long-term sustainability of the company.
Financial ratios allow management to compare the performance of a company or parts thereof with that of competitors and/or other internal departments and that of previous periods.
Financial ratios provide concrete insight into the financial performance of a company to communicate with, among others, investors, lenders and shareholders of the company.


Risks and pitfalls when using ratios
When interpreting ratios, you need to consider various influences, you need to put them in the right context. So consider, among other things:
specific characteristics of the industry
historical and expected company data
changes in company strategy, mergers, acquisitions or restructuring
the economic situation of the past, present and future, market trends, regulations and technological changes
The importance of a financial strategy
By using financial ratios, you know what your financial position is at any given time. And what liquid assets or financial scope your company has to meet (direct) payment obligations.
You can use them to identify and manage financial risks and adjust your strategy, for example by (temporarily) avoiding excessive debts in the event of low(er) solvency.
The ratios show whether there is sufficient financial room to deal with unexpected events such as economic downturns or market fluctuations. In this way, financial stress can be prevented and continuity can be guaranteed.
A healthy ratio of equity versus borrowed capital provides confidence. Based on this, a company can attract capital to invest with.

Good tools are half the battle
Financial reporting software automates the preparation of financial reports, reducing the risk of human error.
Professional financial reporting software offers advanced analysis tools and dashboards, often enabling real-time monitoring of financial data.
With high-quality financial reporting software, such as Speedbooks, you can customize pre-programmed Excel reports based on your own needs. And you can perform scenario analyses and develop predictive models, so that you can anticipate the future and its impact on profitability, solvency and liquidity.
Reliable software is continuously adapted to new reporting requirements and legislation and regulations.
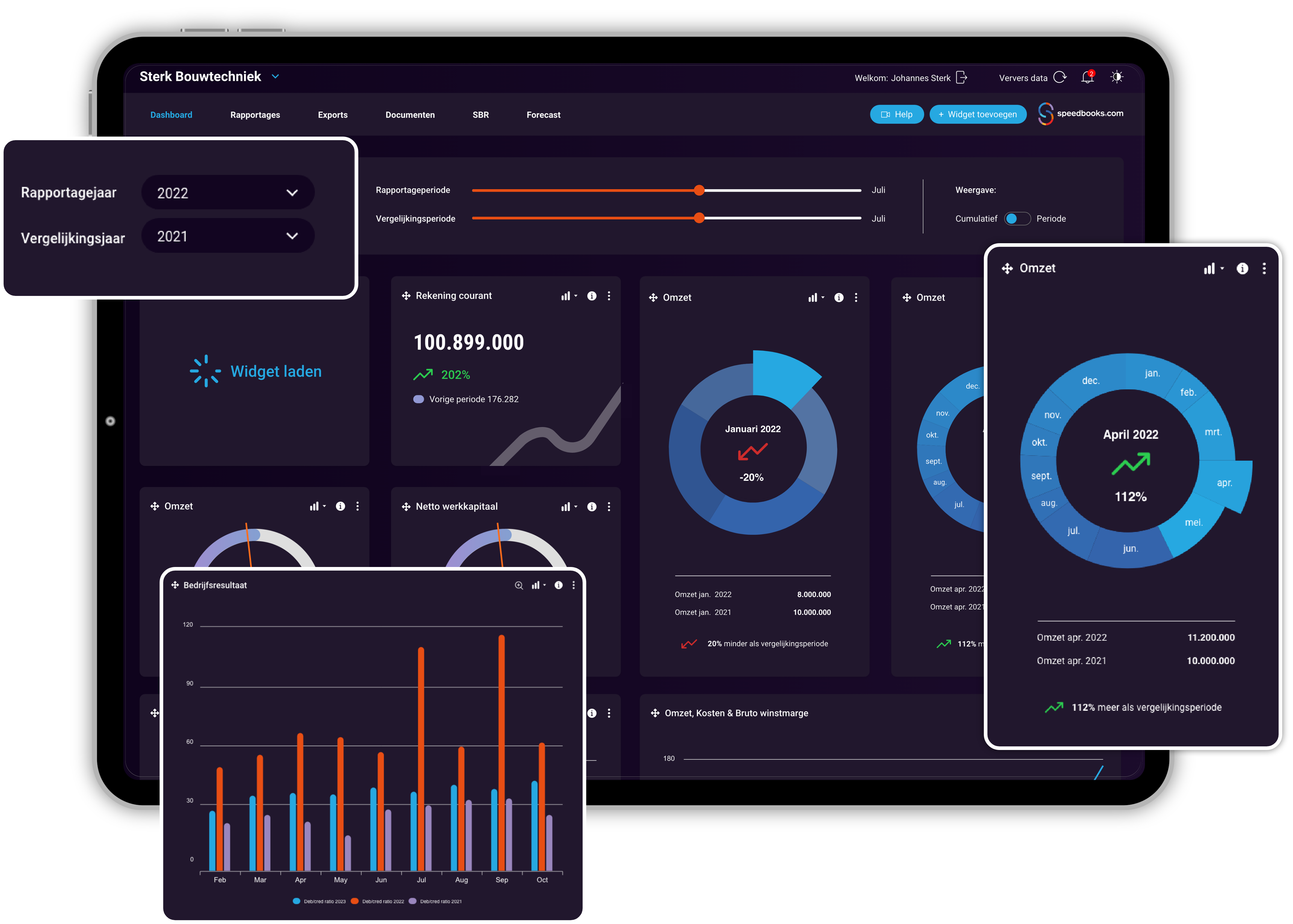
Completely unburdened, everything under control
The reports you create with a professional reporting tool, such as Speedbooks®, meet the above quality requirements.
Speedbooks' modern reporting software can be linked to virtually all accounting systems, so that data collection and analysis is automated, and therefore faster and more efficient.
The collected data can be displayed in real time, both in figures and graphically, in the online financial dashboard and an app. With Speedbooks, you are 'in control' 24/7 and worldwide.
About the author drs. Konstantijn Mikes
Founder, inventor and shareholder of Speedbooks reporting software Konstantijn Mikes (1966) is a graduate economist. He studied Economics at the leading Erasmus University in Rotterdam.
At Speedbooks he is responsible for the content development of the reporting software, and he manages the internal developers and the external developers.

