How to create solid management reporting with reporting software
What is the purpose
A management report is a very important tool for organizations and companies to monitor performance and financial results. To make business decisions based on that.
The purpose of management reporting is to provide executives and managers with up-to-date and relevant information about the (financial) performance of the organization.
After all, management must be well informed in order to determine the right course for the organization.

Informative management reporting is important
The word says it all, it’s about providing information. Management reports provide information about the organization’s performance in the areas of finance, operational performance, human resources, and other relevant matters.
Reports can be periodic, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the organization’s needs. The document provides information about the current situation.
Who do you create management reports for
You basically create a management report for:
- Top management: The highest executives within an organization, such as the CEO (Chief Executive Officer), CFO (Chief Financial Officer), COO (Chief Operating Officer).
- Board of directors: The Board of Directors or Supervisory Board members who supervise the course of business.
- Middle management: Managers who are responsible for specific departments and/or projects within the organization.
- Internal stakeholders: Employees within the organization who are involved in strategic planning, execution and monitoring of objectives.
- External stakeholders: For the information of investors, shareholders, regulators or partners.
Key Performance Indicators, KPIs
Management reports almost always contain KPIs, the so-called:
Key Performance Indicators.
The most important performance indicators, which also show the most important measurable performance of the organization, include turnover, profitability and the efficiency of business processes.

Management reporting content, a KPI overview
Below are the most common general KPIs for management reporting. Depending on the nature of the company or a department, or the project, the requested reporting data by the management, these measurable objectives all or a selection of them are common.
- Sales and Profitability KPIs: Sales Growth, Gross Profit Margin, Net Profit Margin
- Financial Health KPIs: Liquidity Ratios, Solvency Ratios, Cash Flow
- Operational Efficiency KPIs: Cost-Benefit Analysis, Operating Expense Ratio, Asset Efficiency
- Innovation and Growth KPIs: Number of New Products/Services, Growth Rate
- Employee Performance KPIs: Productivity per Employee, Employee Turnover, Cost per Employee
- Quality and Operational Performance KPIs: Quality Measures, Operational Efficiency Indexes
- Market Share and Competition KPIs: Market Share Calculation, Competition Analysis
- Customer Satisfaction KPIs: Customer Satisfaction Scores, New Customer Acquisition, Customer Retention Rate
- Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility KPIs: Environmental Performance, Social Responsibility, Sustainability Goals

How to create correct management reporting, a step-by-step plan
These are the most important steps to create a correct management report:
Step 1: Describe the objectives of the report in concrete terms. What and who do you want to achieve with it. For example: monitoring (financial) performance, identifying opportunities or making strategic decisions.
Step 2: Tailor the content and presentation of the report to the target group. Top management usually needs more strategic (financial) information, middle management needs more detailed information and operational data. Avoid jargon and technical language unless the target group is familiar with it.
Step 3: Choose the right KPIs that accurately reflect the (financial and operational) performance regarding the reporting topic.
Another tip: make the management report readable
Limit the report to the essential, relevant information and the most important points, a clear structure and use graphs, diagrams and other visual elements. Graphs make trends, relationships and patterns quickly recognisable.
Finally, do not provide an extensive report but a concise explanation of the results and performance achieved, the causes, any external sources and the possible implications for the organisation.
Another tip: make management reporting relevant
Use modern tools and technologies, such as professional reporting software, for data analysis and reporting to make the process more efficient.
This ensures that a report meets the expectations of the person(s) for whom the reports are intended and is useful for their decision-making process and possibly prevents a wrong decision.
Risks of misreporting
If the information in a report is not correct, you may miss out on identifying and managing risks. With the right information, you can quickly identify potential problems and take proactive steps to reduce or prevent them.
This also applies to inefficiencies and bottlenecks in business processes. By addressing these issues, organizations can improve their operational efficiency and deploy their resources more effectively.
Internally and externally, trust in the entire organization and/or individuals within the organization can be damaged and decisions can be negatively influenced.
Current financial and performance reporting is a non-stop process
A management report is a snapshot. By updating the data of the report regularly, monthly, quarterly or annually, the information remains relevant.
Also regularly ask for feedback from the recipients of the documents and optimize the form and content of the report when, for example, new, additional or different KPI requirements have arisen.
Next meeting discussed
Management reports also serve as a communication tool within the organization. They help distribute key figures and essentials to different departments and levels of management.
The management report is often the basis of the next meeting. Because the participants are already aware of the current status of different aspects of the business and the main points of discussion, meetings can be held and decisions made efficiently.

Discussion, determining or adjusting strategy
A management report can also serve as a basis for 'healthy' discussion during the meeting and for exchanging ideas and insights about trends, opportunities and threats.
Keeping your finger on the pulse continuously through periodic (financial) management reports makes it possible to adapt strategies to changing circumstances and market conditions.
The entire management of the organization remains sharp and alert.
Who else do you make management reporting for
Managers and business directors must be accountable internally to senior management, a board of directors or supervisory board, shareholders and other stakeholders. With correct management reporting with (only) the necessary relevant information, you can meet this accountability obligation.
Various interested parties or so-called stakeholders, such as investors, creditors and lenders, expect transparency about the finances and performance of an organization through regular reporting.
In summary, the quality requirements for high-quality reporting
A high-quality management report has a concise layout and an overview of what is in the report. This allows directors to immediately browse to the desired information, which you formulate briefly and concisely.
It should only contain relevant figures and information that are directly related to the objectives and strategies of the organization. Unnecessary details can distract from the most important points.
All information in the report must be accurate and reliable. The use of up-to-date data and accurate measurements is essential to maintain the trust of the readers.
The report must be available on time and regularly (periodically), so that managers can make the right decisions in response to current events and potential problems, but also to opportunities and trends.
A good management report must be flexible, so that it can be adapted to changing management needs, for example by adding new KPIs.
Finally, the management report must also contain forward-looking information, such as (financial) forecasts and plans.
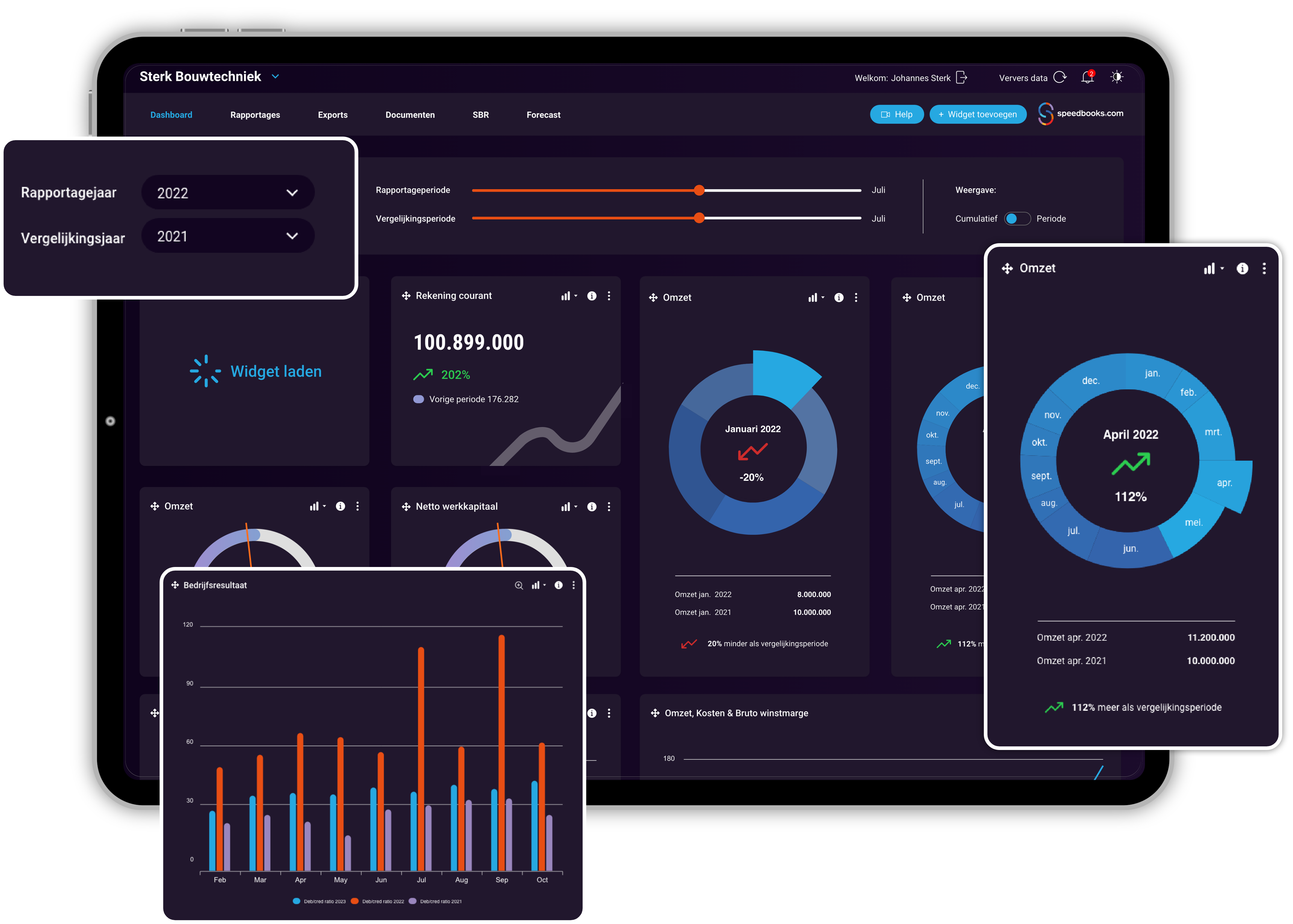
Only use professional reporting software
Professional reporting software, such as Speedbooks, offers advanced functionalities and tools that make it easier to process, analyse and present complex data.
Speedbooks connects to various data sources and systems, including virtually all accounting software and databases. This ensures accurate and up-to-date data in the reports.
The (sample) reports are based on Excel. This allows users to create customised reports based on specific needs and requirements of the management team.
Speedbooks is regularly updated with new features and improvements, so that the software remains up-to-date and you can benefit from the latest technological developments.

About the writer drs. Konstantijn Mikes
Founder, inventor and shareholder of Speedbooks reporting software Konstantijn Mikes (1966) is a graduate economist. He studied Economics at the leading Erasmus University in Rotterdam.
At Speedbooks he is responsible for the content development of the reporting software, and he manages the internal developers and external developers.
